How to operate a drone is a question many ask, opening a world of exciting possibilities from aerial photography to advanced maneuvers. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced techniques and troubleshooting. We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, delve into safety procedures, and show you how to capture stunning aerial footage.
Whether you’re a beginner or looking to enhance your skills, this comprehensive resource will empower you to confidently take to the skies.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding the various parts and their functions to mastering advanced flight techniques. We’ll also cover important safety considerations and legal regulations, ensuring you fly responsibly and legally. Through clear explanations, practical examples, and helpful tips, this guide will transform you into a skilled and confident drone pilot.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key parts and their functions, along with variations in design and impact on flight.
Main Drone Components and Their Functions
A typical drone consists of several key components working in concert. These include the frame, motors, propellers, electronic speed controllers (ESCs), flight controller, battery, and the onboard camera. The frame provides the structural support for all other components. Motors provide the thrust, while propellers convert rotational energy into lift. ESCs regulate the power to the motors.
The flight controller is the brain of the operation, processing sensor data and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. The battery provides the power for all components, and the camera captures the aerial footage.
The Flight Controller’s Role
The flight controller is a sophisticated mini-computer that acts as the central nervous system of the drone. It receives data from various sensors such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, barometers, and GPS (if equipped), and uses this information to adjust the speed of each motor individually, maintaining stability, altitude, and direction. It also processes commands from the remote controller, translating them into precise motor adjustments.
Drone Propeller Types and Flight Performance
Drone propellers come in various designs, each impacting flight characteristics. The key factors are size (diameter and pitch), material (plastic or carbon fiber), and number of blades (typically 2, 4, or 6). Larger propellers generally provide more lift and slower speed, while smaller propellers offer greater speed and maneuverability. Carbon fiber propellers are typically stronger and lighter than plastic propellers.
The number of blades influences efficiency and noise levels.
Comparison of Three Drone Models
| Feature | Drone A | Drone B | Drone C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Flight Time | 25 minutes | 30 minutes | 20 minutes |
| Camera Resolution | 4K | 1080p | 4K |
| Max Speed | 60 km/h | 70 km/h | 50 km/h |
| Weight | 750g | 850g | 600g |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is essential to ensure safe and successful operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, calibrating sensors, and confirming compliance with local regulations.
Pre-Flight Drone Inspection Checklist

- Visually inspect the drone’s frame for any damage.
- Check the propellers for damage or looseness.
- Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected.
- Verify that all other components are securely attached.
- Power on the drone and remote controller, checking for any error messages.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check GPS signal strength (if applicable).
- Confirm the drone’s location is legal and safe for flight.
Sensor Calibration Importance
Calibrating the drone’s sensors before each flight is critical for accurate and stable flight. This ensures the flight controller receives accurate data from the accelerometers, gyroscopes, and compass, enabling precise control and preventing unexpected movements.
Drone Flight Regulations
Drone regulations vary significantly depending on location. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying. This often includes restrictions on flight altitude, distance from obstacles, and airspace restrictions near airports or other sensitive areas. Failure to comply can result in fines or legal consequences.
Pre-Flight Preparation Flowchart, How to operate a drone
A flowchart visually represents the sequential steps involved in pre-flight preparation. It begins with a power-on check, proceeds through sensor calibration and component inspection, and concludes with confirmation of legal flight parameters.
Basic Drone Operation and Controls
Understanding the controls and basic maneuvers is the foundation of safe and effective drone operation. This section covers takeoff, landing, altitude control, direction control, and basic maneuvers.
Drone Remote Control Functions
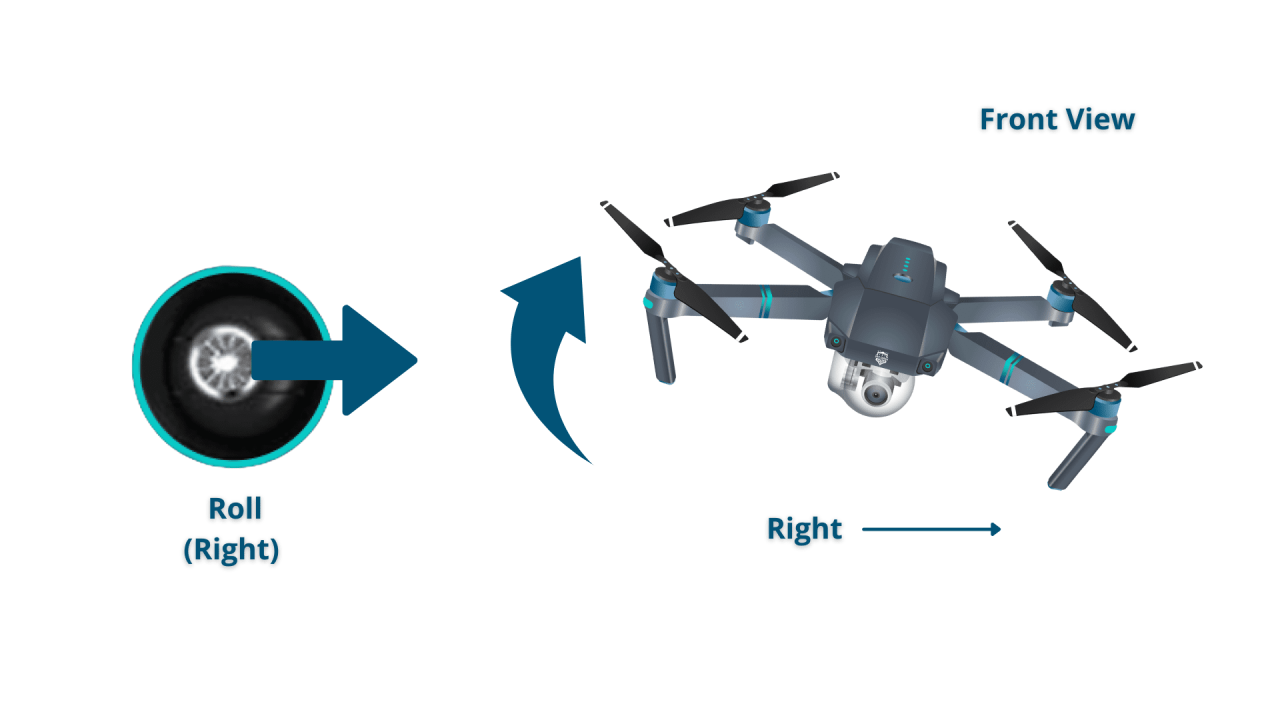
Standard drone remotes typically feature two control sticks and several buttons. The left stick generally controls altitude and yaw (rotation around the vertical axis), while the right stick controls roll (rotation around the longitudinal axis) and pitch (rotation around the lateral axis). Buttons are used for functions like takeoff/landing, camera control, and flight mode selection.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Takeoff and landing should be performed in a controlled and deliberate manner. Begin by ensuring the drone is in a clear, open area, away from obstacles. For takeoff, gently push the left stick upwards to ascend slowly. For landing, gently lower the left stick to descend slowly, maintaining control until the drone touches down gently.
Altitude, Direction, and Speed Control
Altitude is controlled by the vertical movement of the left stick. Direction (yaw) is controlled by rotating the left stick left or right. Speed is often controlled by a throttle dial or a separate lever on the remote controller. Smooth and gradual adjustments are key to maintaining control.
Basic Maneuvers: Hovering and Turning
Hovering involves maintaining a stable position in the air. This requires precise control of the sticks to counteract any external forces, such as wind. Turning involves adjusting the yaw using the left stick while maintaining altitude and forward speed. Smooth, gradual inputs are crucial for precise maneuvers.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers and Techniques
Once comfortable with basic operation, pilots can explore more advanced maneuvers and techniques to enhance their flying skills and capture creative footage.
Advanced Flight Techniques: Flips, Rolls, and More
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, require practice and a good understanding of the drone’s response to control inputs. These maneuvers involve rapid and precise movements of the control sticks, and should only be attempted in a safe and open environment, away from obstacles and people.
Smooth and Precise Drone Control
Achieving smooth and precise drone control requires practice and patience. Focus on making small, gradual adjustments to the control sticks, rather than abrupt movements. This allows for better control and reduces the risk of accidents.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions presents significant challenges. Strong winds can push the drone off course and make it difficult to maintain stability. It’s often recommended to avoid flying in strong winds, but if necessary, increase your awareness of wind direction and adjust your flight accordingly. Using a drone with advanced wind resistance features can help mitigate these challenges.
Flight Modes: GPS vs. Attitude Mode
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control. GPS mode utilizes satellite data to maintain position and altitude, offering greater stability, especially in windy conditions. Attitude mode relies primarily on onboard sensors, allowing for more agile maneuvers but potentially less stability in windy conditions.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography, allowing for stunning aerial shots. This section explores camera settings, shot composition, and best practices for capturing high-quality footage.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, aperture, and white balance significantly impact image quality. Adjusting these settings based on lighting conditions and desired aesthetic is crucial for achieving optimal results. Higher ISO values are suitable for low-light conditions, while lower ISO values are preferable in bright light. Shutter speed should be adjusted to avoid motion blur.
Composing Shots and Framing Subjects
Effective composition is crucial for compelling aerial photography and videography. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional principles to create visually appealing shots. Framing your subjects effectively highlights them and enhances the overall impact of the image.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Drones allow for unique camera angles and perspectives unattainable with traditional methods. Experiment with different angles, such as high-angle shots, low-angle shots, and dynamic tracking shots, to add variety and visual interest to your footage.
Best Practices for Stunning Aerial Photography and Videography
- Plan your shots carefully.
- Use a variety of angles and perspectives.
- Pay attention to lighting conditions.
- Practice smooth and precise drone control.
- Edit your footage to enhance its impact.
Drone Battery Management and Safety

Proper battery management is essential for extending battery life and ensuring safe drone operation. This section details charging, storage, and safety precautions.
Charging and Storing Drone Batteries
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow their instructions carefully. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries, as this can damage them and reduce their lifespan. Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
Signs of a Failing Drone Battery
Signs of a failing drone battery include reduced flight time, unusual heating, swelling, or leakage. If you notice any of these signs, discontinue use immediately and replace the battery.
Potential Safety Hazards and Mitigation
Potential safety hazards associated with drone operation include collisions with obstacles, loss of control, and battery fires. To mitigate these risks, always fly in a safe and open area, away from obstacles and people. Regularly inspect the drone and its components for any damage, and use appropriate safety gear.
Battery Specifications Table (Example)
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Capacity | 5000 mAh |
| Voltage | 14.8V |
| Charging Time | 60 minutes |
| Flight Time | 25 minutes |
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section addresses common drone malfunctions and provides troubleshooting steps for resolving them.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common drone malfunctions include unresponsive controls, low battery warnings, GPS signal loss, and motor failures. These issues can be caused by various factors, including low battery, interference, sensor problems, or physical damage.
Troubleshooting Steps for Common Problems
Troubleshooting steps typically involve checking battery levels, ensuring proper connections, calibrating sensors, and restarting the drone. If problems persist, consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or seek professional assistance.
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning Tips
Regular maintenance and cleaning are crucial for preventing issues and extending the lifespan of the drone. This includes cleaning the propellers and body, inspecting for damage, and lubricating moving parts (as recommended by the manufacturer).
Handling Emergency Situations
In emergency situations, such as unexpected power loss or loss of control, prioritize safety. Attempt to regain control if possible, but if the situation cannot be resolved safely, consider activating emergency landing procedures (if available) or allowing the drone to land gently, prioritizing safety over equipment.
Drone Flight Simulation and Practice
Drone simulators provide a safe and controlled environment to practice flying skills before venturing into real-world flights.
Benefits of Drone Simulators
Drone simulators offer several benefits, including the ability to practice in a risk-free environment, learn advanced maneuvers, and improve piloting skills without the cost and risk of damaging a physical drone. They are especially helpful for practicing emergency procedures and handling challenging situations.
Recommended Drone Simulator Software
Several reputable drone simulator software options are available, offering realistic flight dynamics and various environments for practice. Some popular examples include [mention specific simulator names, briefly describing their key features].
Improving Piloting Skills and Safety with Simulators
Consistent practice in a simulator can significantly improve piloting skills, hand-eye coordination, and decision-making abilities under pressure. This translates to safer and more controlled real-world flights.
Transitioning from Simulator to Real-World Flights
When transitioning from simulator practice to real-world flights, start with basic maneuvers in a safe, open area. Gradually increase the complexity of your flights as your confidence and skill improve. Always prioritize safety and be prepared to land immediately if needed.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has equipped you with the fundamental understanding and practical skills necessary for safe and effective drone piloting. Remember that continuous practice and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for honing your skills and ensuring a positive flight experience. Embrace the challenges, celebrate your successes, and explore the boundless possibilities that await you in the world of drone technology.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the fundamentals, which you can easily do by checking out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From there, practice is key to mastering the skills needed for safe and effective drone operation, ensuring you’re comfortable with the technology before taking flight.
Happy flying!
Essential FAQs: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are excellent for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and automated flight modes. Look for models with good reviews and a strong reputation for ease of use.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and ensure you’re flying responsibly and legally.
Proper training is crucial before operating any drone, so invest time in learning the fundamentals.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and procedures. Registration often involves providing drone information and personal details.
What is the maximum flight time for a typical drone battery?
Flight times depend heavily on the drone model and battery size. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge for many consumer drones. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for your specific model.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, prioritize safety. Attempt to regain control using the emergency stop function if available. If unable to regain control, let the battery drain and the drone will land. Report the incident to relevant authorities if needed.
